The evolving landscape of financial technology is presenting new opportunities for sending and receiving money internationally. The rise of stablecoins has generated a promising avenue for cheaper remittance solutions. However, discrepancies in conversion costs across regions complicate the narrative. A recent study reveals that conversion rates for stablecoin transactions vary significantly, with Africa facing some of the steepest costs compared to other global regions.
Understanding Regional Conversion Costs
Data shows that remittance fees within Africa can be exorbitantly higher than those in places like Latin America and Asia. For instance, South Africa enjoys a more competitive market environment, resulting in lower conversion rates, generally around 1.5%. Here, numerous financial service providers create healthy competition, enhancing liquidity.

In stark contrast, countries such as Botswana and the Democratic Republic of the Congo experience conversion spreads that can soar to nearly 19.4% and 13%, respectively. These findings are based on extensive datasets that analyzed over 66 currency corridors, indicating systemic issues rather than isolated incidents.
The Role of Market Dynamics
This data underscores the importance of market dynamics in determining conversion rates. The presence of multiple financial institutions leads to lower costs, while monopolistic scenarios can inflate prices significantly. Essentially, the spread—the difference between a provider’s purchasing and selling price for stablecoins—directly influences the fees consumers must pay.
Many reports suggest that it is not the technology behind blockchain or stablecoins that creates these high costs but rather local market limitations and liquidity issues. This means enhancing competition locally is crucial for lowering fees.
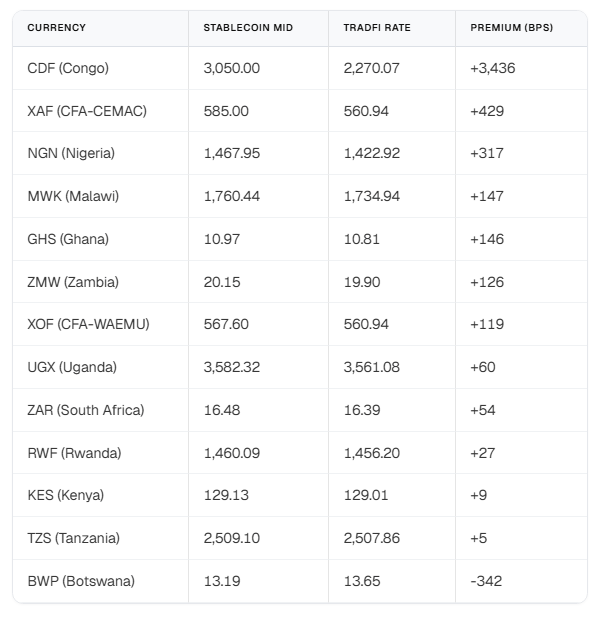
Stablecoins vs. Traditional Currency Exchange
Further investigations from various financial research entities shed light on how stablecoin rates compare with traditional foreign exchange (FX) rates. Despite a global median difference of about 0.05%, African markets experience a notable gap of roughly 1.2%. This further complicates the expectation that stablecoins would naturally lead to lower costs in all corridors.
Implications for Consumers and Market Development
Economists highlight the potential of stablecoins to reduce remittance costs when compared with traditional services that can charge around $6 for every $100 sent. However, the reality remains nuanced. While faster transactions and lower fees are attainable, success hinges on efficient local on-ramps and off-ramps for currency exchange.
For regulators and new market entrants, the findings are clear—there is an urgent need to bolster local market competition and enhance liquidity, parallel to improving cross-border transaction systems.
Indeed, while stablecoins hold promise for a more affordable and efficient monetary exchange, the practical challenges in local conversions linger, emphasizing the importance of domestic market factors.
Featured image from andBeyond, chart from TradingView



